Secure Virtual Architecture (SVA)
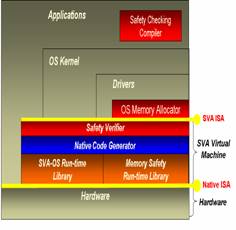 Secure Virtual Architecture (SVA) is a compiler-based virtual machine
capable of hosting an entire commodity operating system and all its
applications. The virtual machine is unique because it combines a
sophisticated compiler (like high-level language virtual machines such
as JVM or CLI) with a rich run-time system capable of monitoring and
controlling all privileged operations (like Virtual Machine Monitors
such as VMware or Xen). This combination opens up the opportunity to
develop novel and powerful solutions to a wide range of important
software security and reliability problems, including intrusion
prevention, intrusion detection and analysis, OS component isolation,
full system recovery, application data confidentiality, secure
application- and system-level information flow, and many others.
Secure Virtual Architecture (SVA) is a compiler-based virtual machine
capable of hosting an entire commodity operating system and all its
applications. The virtual machine is unique because it combines a
sophisticated compiler (like high-level language virtual machines such
as JVM or CLI) with a rich run-time system capable of monitoring and
controlling all privileged operations (like Virtual Machine Monitors
such as VMware or Xen). This combination opens up the opportunity to
develop novel and powerful solutions to a wide range of important
software security and reliability problems, including intrusion
prevention, intrusion detection and analysis, OS component isolation,
full system recovery, application data confidentiality, secure
application- and system-level information flow, and many others.
SVA currently uses techniques employed by the SAFECode compiler to provide strong memory safety guarantees to the Linux kernel. All software in SVA is compiled down to a virtual instruction set; SVA translates code from the virtual instruction set to the native processor's instruction set transparently. SVA's virtual instruction set is the LLVM IR enhanced with additional instructions to provide memory safety for low-level software/hardware interactions.
